What is the difference between arthritis from arthrosis, you need to know not only doctors.Often engaged in self -medication, people expose themselves to great risk, taking one disease for another.Such an error can lead to serious complications, so in the article we thoroughly analyze the differences in the symptoms, the features of treatment, and the prevention of pathologies.Knowing the symptoms will help to take the necessary measures in a timely manner.With arthritis or arthrosis, all our mobile compounds at the site of the joint of the bones, cartilage, i.e.The joints of the skeleton.Often, diseases confuse with each other due to consonant names, but the difference between them is not only in the symptoms, but in the causes of occurrence, features of the course, specifics of therapy.
What is the difference between arthritis and arthrosis: a general concept
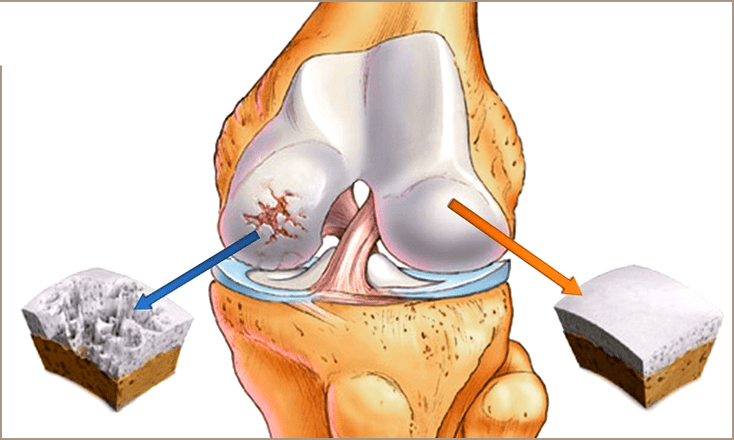
In the names there is a common root of “Artro”, translated from Greek means a joint that is subjected to basic disorders.However, arthrosis does not have an inflammatory nature, the basis is degenerative processes, i.e.The wear, and the correct designation of the disease is osteoarthrosis, since bone formations are subjected to changes.
Arthrosis is a chronic disease in which the “erasing” of articular surfaces and capsules occurs, due to which the deformation begins.In advanced cases - complete immobilization of the limb.The changes affect the whole complex - bone surfaces, ligaments, meniscus, cartilage, synovial shell, all structures located nearby.
Pathologies are subjected to older people.Moreover, the older, the more the prevalence of the disease increases.In rare cases, young people can affect young people with hereditary signs or after an injury.According to statistics, about 10% of the population suffers, and the main threshold is observed in people over 65 years old (85% of all patients).
Arthritis, on the contrary, is an acute disease, which is based on inflammation.Often, the ailment is only a symptom of the underlying disease (rheumatism), but can proceed as a only violation.The neglected stages are transferred to a chronic flow.Unlike arthrosis, young people are most often undergoing inflammatory damage.It can manifest itself after 40 if a person has suffered a serious cold or infection.The prevalence among the population of the globe is only 2%.
Reasons
Due to various etiologies, different causes and factors lead to the occurrence of diseases.Moreover, arthrosis often occurs against the background of purulent arthritis or rheumatism.
The main factors of arthritis.
- Trauma and surgical joint interventions.
- Congenital dysplasia (underdevelopment) of the joints.
- Dostrophically depth processes.
- Excess weight.
- Elderly age.
- Heredity.
- Klimax.
With this ailment, the joints suffer exclusively, while with arthritis there is a general inflammatory process.Often it is accompanied by damage to the kidneys, heart and liver.
Several types of disease are distinguished:
- rheumatoid;
- reactive;
- infectious;
- gout.
Very often, arthritis arise against the background of the transferred influenza, frequent sore throats.Development of tuberculosis, gonorrhea, dysentery, psoriasis is not excluded.
Arthritis rarely affects single joints, usually an entire group is subjected to inflammation, which depends on etiology - with rheumatism, small compounds of the hands and feet suffer, with psoriasis - phalanges of the fingers.
Symptoms
Despite similar signs - pain, restriction in movement, deformation, there are a number of symptoms that help distinguish between the name of the disease.
- Pain is a leading sign of arthrosis, but does not occur immediately.Initially, this is a crunch and cracking of the joints, and then pain is joined, which increase as they progress.They usually appear with physical exertion, weather change, at night (starting pain - immediately after awakening and attempts to get out of bed).Arthritis is characterized by constant aching pain, which can intensify at night, as well as in the morning.Often, with inflammation, there is a decrease in unpleasant symptoms during active movements.
- Cryst is a specific sign of arthrosis.It has a special sound - dry and rough, is often accompanied by sharp pain.
- Deformation - with degenerative changes, the joints change in the later stages, when adjacent bone surfaces are included in the process.With inflammation, the deformation begins at the earliest stages, while they increase in size due to swelling.
- Redness, an increase in local temperature - is characteristic only for arthritis, since degenerative diseases proceeds according to the type of aseptic (without infectious) necrosis.
- Restriction in motion - arthrosis often “blocks” the joint when, when moving, a sharp crunch is distributed, followed by a sharp pain and joint block.Arthritis has a tendency to morning stiffness, not only in the joints, but in the whole body.
- General malaise - inflammation, always proceeds with a change in the state of the whole organism, there is an increase in body temperature, weakness.
Almost all joints can affect the localization of the ailments, however, damage to the knee and hip is more characteristic of degenerative processes.Arthritis has a tendency to involve small joints of the arms and legs in inflammation, often symmetrically.
Important: do not confuse the crunching of healthy joints with arthrose.In the first case, it is absolutely painless and are associated with the features of the ligamentous apparatus (excessive mobility, weak ligaments).Then, as with arthrosis, crunch is accompanied by severe pain and restriction in motion.
Diagnostics
An important diagnostic criterion is a general blood test.Inflammation of the joints always gives an increase in ESR (more than 25 mm/h), and in the case of infectious arthritis, leukocytes are still.For arthrosis, the change in blood is not characteristic.
By the way, there is a special protein, belongs to the class of immunoglobulins, reacts to damage by any factor in its own cells-a rheumatoid factor that allows you to determine the presence of rheumatoid arthritis.C-reactive protein, which is a sign of inflammation, is also determined.Gout is characterized by an increase in uric acid in the blood, urine.
For both diseases, first of all, it is necessary to pass not only a blood test, always an X -ray picture of the joint.With arthrosis, a narrowing of the gap between the joints, osteophytes (bone growths), deformations and osteoporosis occurs.It is possible to appoint CT, MRI to clarify changes in soft tissues and bone structures.
Arthrosis is also characterized by a narrowing of the gap and periarticular osteoporosis, however, they occur in the early stages (then, as with degeneration, such changes begin only at 3 and 4 stages).If the process has an infectious character, sequesters are often formed - areas of necrosis surrounded by a healthy tissue.In a chronic course, dislocations are observed, subluxation of hinged structures.
It is advisable to conduct an ultrasound in order to determine the presence of a liquid or pus in the joint bag (most characteristic of arthritis), as well as diagnostic punctuation - allows you to identify the pathogen and the nature of the effusion.
Be sure to prescribe general examinations - ECG, urine analysis, blood biochemistry, to learn about their possible inclusion in inflammation.
Treatment
Important: the most dangerous for both diseases is self -medication.Without an accurate diagnosis, this approach to its health only worsens the situation, leading to a significant destruction of the joints, damage to the heart and kidneys.
How arthritis differs from arthrosis in the therapy.The basis for the first is the stop of destruction, degeneration of cartilage tissue, and in the treatment of arthritis, the main role is devoted to the removal of inflammation and blocking the infectious process.
The approach to eliminating the manifestations of pathologies should include not only medicines, but also a change in lifestyle - healthy nutrition, weight loss, physical activity control.
Drug therapy includes non -steroidal anti -inflammatory (necessary for both diseases), muscle relaxants and chondroprotectors (more often with arthrosis).
Treatment of arthritis often requires the introduction of glucocorticosteroids into the intersection space, the use of antibiotic therapy, and plasma -function (blood purification) to eliminate autoagresia (the body's reaction to its cells, as to a foreign agent).In severe cases, the introduction of stem cells is carried out - it relieves inflammation, reduces susceptibility to infection, improves metabolism and tissue nutrition.
Important: with arthritis, warming compresses and ointments cannot be applied, they will only increase the spread of infection and inflammation, especially with the purulent course of the disease.
All physiotherapy is prescribed only after removing acute pain and inflammation.
Despite all the innovations and the rapid development of medicine, arthrosis is an incurable disease.It is simply not possible to fix the degenerative changes that have begun.Arthritis succumbs to therapy well, especially when seeking a doctor.
Conclusion in the table
| Differences |
Arthritis |
Arthrosis |
| Age | Unlimited | Mainly after 45 |
| The development of pathology | Suddenly | Gradually |
| Reasons | Infectious | Degenerative (age, menopause, injuries, genetics) |
| Flow | Acute, with moments of remission | Chronic, with periods of exacerbations |
| Defeat | From small to large ones.Symmetry is characteristic. Ligaments, meniscus with severe inflammation, swelling are involved. Internal organs suffer. |
More often large single.The risk of the phalanx of the thumbs.It spreads to the cartilage, meniscus, ligaments, but without edema. |
| Deformation | External increase due to swelling. | In the late stages, the formation of necrotic fragments, subsequently destroyed |
| Signs | In the acute period - malaise with temperature, a sharp crunch with pain and lock, a swollen hot surface, a pronounced difficulty in movements. | It's a dull pain.Heaviness, stiffness after charging retreats. |
| Diagnostics | General blood test, urine.Biochemical - blood. X -ray testimony is a sharp change in structures at the onset of the disease. |
Minor changes in blood.X -ray shows the pathology in the later stages. |
| Treatment | Anti -inflammatory, painkillers.It is cured with timely handling. | Anesthetizing, ointments, compresses, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, chondroprotectors. With exacerbation - anti -inflammatory. |
What is worse than arthritis or arthrosis cannot be said for sure, but inflammation is well blocked by medicines, which cannot be said about degenerative processes.Often, both diseases must be treated all your life, with the possibility of achieving long -term remission.Arthrosis often needs operational correction to return the function of the joint and remove the restriction in movements.
Arthritis may be accompanied by the development of heart defects (rheumatoid damage to the valves) and diseases of other organs and systems, because inflammation of the joints is just the “tip of the iceberg”.Successful treatment begins precisely with the definition of etiology.
It is important to prevent late stages from the destruction of bone tissue and the chronic inflammatory process.Timely appeal to a specialist will help to accurately learn his own diagnosis, as well as get the necessary assistance in treatment and rehabilitation.Now you know what is the differences between arthrosis and arthritis.



















